The SUNLIT team (C2N), in collaboration in particular with researchers at the German Fraunhofer ISE, has succeeded to trap sunlight efficiently in a solar cell thanks to an ultrathin absorbing layer made of 205 nm-thick GaAs on a nanostructured back mirror. With this new architecture, an efficiency of nearly 20% was obtained. The results are published in Nature Energy.
Up to now, the laboratory state-of-the-art 20%-efficient solar cells required at least 1 micrometer-thick layers of semiconductor material (GaAs, CdTe or copper indium gallium selenide -CIGS-), or even 40 µm or more in the case of silicon. A significant thickness reduction would enable material savings of scarce materials like Tellerium or Indium and industrial throughput improvements due to shorter deposition times. However, thinning absorber automatically reduces absorption of sunlight and conversion efficiency. A flat mirror at the backside of the cell can help and lead to double-pass absorption, but no more. But previous attempts of light trapping have been greatly limited in performance by the optical and electrical losses.
Researchers of the team led by Stéphane Collin and Andrea Cattoni at the Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies – C2N (CNRS/University Paris-Saclay), in collaboration in particular with the Fraunhofer ISE, have developed a new strategy to trap light in ultrathin layers made of only 205 nm-thick gallium arsenide, a semiconductor of the III-V family. The guiding idea was to conceive a nanostructured back mirror to create multiple overlapping resonances in the solar cell, identified as Fabry–Perot and guided-mode resonances. They constrain light to stay longer in the absorber, resulting in efficient optical absorption despite the low quantity of material. Thanks to numerous resonances, absorption is enhanced over a large spectral range that fits the solar spectrum from the visible to the infrared.
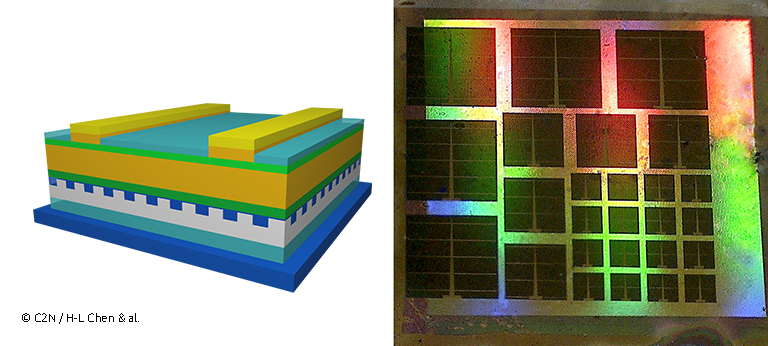
Controling the fabrication of patterned mirrors at the nanometer scale has been a key aspect of the project. The team used nanoimprint lithography to emboss directly a sol-gel derived film of titanium dioxide, an inexpensive, rapid and scalable technique.
Can ultrathin solar cells be further improved? The work published in Nature Energy demonstrates that this architecture should enable 25% efficiency in the short term. Even if the limits are still unknown, we are convinced that the thickness could be further reduced without efficiency loss, at least by a factor of two. GaAs solar cells are still commercially limited to space application due to their cost. However, we are already working to extend this concept for large-scale photovoltaics made of CdTe, CIGS (ARCIGS-M H2020 project) or silicon materials.
References:
A 19.9%-efficient ultrathin solar cell based on a 205-nm-thick GaAs absorber and a silver nanostructured back mirror,
Hung-Ling Chen1, Andrea Cattoni1, Romaric De Lépinau1,2, Alexandre W. Walker3, Oliver Höhn3, David Lackner3, Gerald Siefer3, Marco Faustini4, Nicolas Vandamme1, Julie Goffard1,2, Benoît Behaghel1, Christophe Dupuis1, Nathalie Bardou1, Frank Dimroth3 & Stéphane Collin1,2
Nature Energy (2019)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0434-y
1 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies – C2N (CNRS / University Paris-Sud/Paris-Saclay)
2 Institut Photovoltaïque d’Ile-de-France (IPVF)
3 Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE)
4 Laboratoire Chimie de la Matière Condensée de Paris – LCMCP (Sorbonne Université / CNRS / Collège de France)



